With the rapid development of advanced technologies such as cloud computing and big data analysis, enterprises and process automation factories have more capabilities to solve various challenges. Many enterprises are rapidly developing their business using the Internet service model.
Cloud computing leverages virtualized and fixed computer resources to provide customers with solutions that enable global information services with minimal up-front investment. In addition, advances in these technologies are being made to facilitate industries such as big data analytics that organize, summarize, and analyze high-volume and diverse data. There are many applications of cloud computing in the field of industrial automation, including historical data, status maintenance, predictive maintenance, asset management and more.
This article will analyze how cloud computing technology translates into value to help future automation factories boost productivity.
The basic composition of cloud computing
Cloud computing is a model of network access that requires a set of shared computing resources such as servers, networks, storage devices, software applications, and clients. This is what all business managers need by interacting with service providers through efficient computing resource allocation.
The target customer needs are flexible, cloud-based services have on-demand usage, pay-per-use and multi-tenant characteristics. Therefore, there are three types of cloud computing services: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
Cloud services can be divided into four categories, namely public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, community cloud. The most commonly used model is a hybrid model, a basic combination of two or more clouds that includes a variety of public, private, and community clouds. Public non-critical services often use the public cloud, and company-specific and specialized services using private cloud execution.
The combination of a large number of technologies makes cloud computing a reality for industrial automation services, including virtualization, utility computing, distributed computing, and grid computing. Virtualization enables multiple clients to share physical resources such as hardware and software, human resources and knowledge.
Cloud data collation and analysis
It can be seen that cloud computing has made leaps and bounds in various applications and has a huge impact on the industrial automation industry. It can help improve data management efficiency and equipment performance, and cloud computing technologies have opened up new opportunities in the industry.
In the past, unpredictable future events due to lack of data and predictive data models, today, these production models have been deployed to collect large amounts of data through the Internet of things, analytical tools to deal with the data for managers to provide the best decision-making reference.
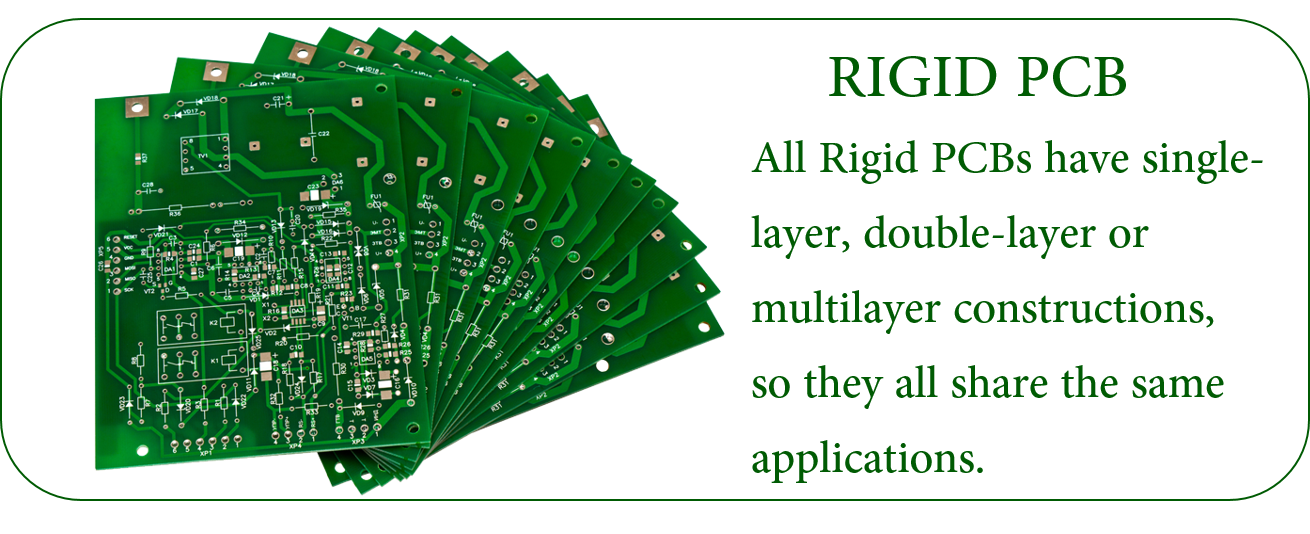
Rigid PCB
Rigid PCB, the largest number of PCB manufactured
What is Rigid PCB - Rigid PCB Definition
Rigid PCB is a kind of printed circuit board, and is the largest number of PCB manufactured. It is made of solid substrate material, which can effectively prevent the distortion of the circuit board. Perhaps the most common rigid circuit board is the computer motherboard. The motherboard is a multi-layer PCB designed to distribute power from the power supply while allowing communication between all components of the computer, such as CPU, GPU and RAM.
Rigid PCB can be used in any position where the PCB itself needs to be set to a shape and maintained during the remaining life of the equipment. Rigid PCBs can be anything from simple single-layer PCBs to eight or ten-layer multi-layer PCBs.
Rigid PCB and Flexible PCB are totally different. One is flexible and the other is rigid. Therefore, their application scenarios are different. In addition, there are rigid-flex PCB. There are similarities between them. However, all rigid PCB have single-layer, double-layer or multi-layer structure, so they have common application scope. This is the case.
Some characteristics of rigid PCB
- Rigid PCB is a kind of conventional PCB, which can not be like flexible PCB, because rigid PCB can not be twisted or folded into any shape, because it has FR4 reinforcement, which is very useful for increasing stiffness.
- Rigid PCB is made up of copper trances and paths which are incorporated on a single board in order to connect the different components on the board. The base material of the board is made of rigid substrate which gives rigidity and strength to the board.
- The computer motherboard is the best example of a rigid PCB with a rigid substrate material.
- Once rigid PCBs are manufactured, they cannot be modified or folded into any other shape.
- Rigid PCB is cheaper than flexible PCB. They are traditional PCBs and are widely used in many electronic products.
- Flexible PCB and rigid PCB have their own limitations and advantages in terms of ease of use and availability. Both of them are used to connect multiple electronic components on circuit boards.
Rigid PCB manufacturing
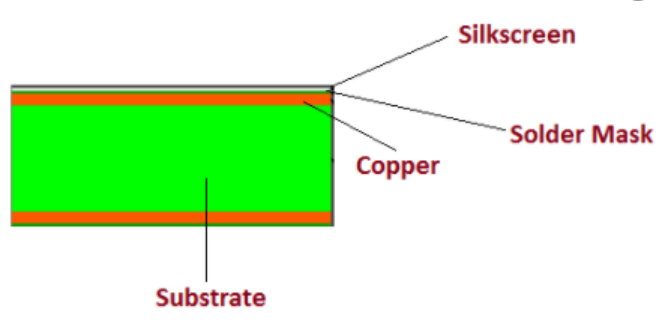
Rigid PCB is made up of different layers that are joined together using adhesive and heat, providing a solid shape to board material. Following layers are used to develop a rigid PCB.
Substrate Layer - rigid PCB material
- Substrate layer, also referred base material, is made of fiber glass.
- The FR4 is mostly used as a substrate material which a most common fiber glass that provides rigidity and stiffness to the board.
- Phenilcs and epoxies are also used as a base material but they are not as good as FR4, however, they are less expensive and feature unique bad smell.
- Decomposition temperature of phenolics is too low that results in delamination of the layer if solder is placed for long duration of time.
Multilayer Rigid PCB Stackup
Copper Layer
- On the top of substrate layer, there resides a copper foil which is laminated on the board with the help of added amount heat and adhesive.
- In common use, both sides of the board are laminated with copper, however, some cheap electronics come with only one layer of copper material on the board.
- Different boards come with different thickness which is described in ounces per square foot.
Solder Mask Layer
- Solder Mask Layer houses above the copper layer.
- This layer is added on the board to add insulation on the copper layer in order to avoid any damage in case any conduction material is touched with the copper layer.
Silkscreen Layer
- Silkscreen layer is located above solder mask layer.
- It is used to add characters or symbol on the board that provide better understanding of the board.
- White color is mostly used for silkscreen however, other colors are also available including grey, red black and yellow.
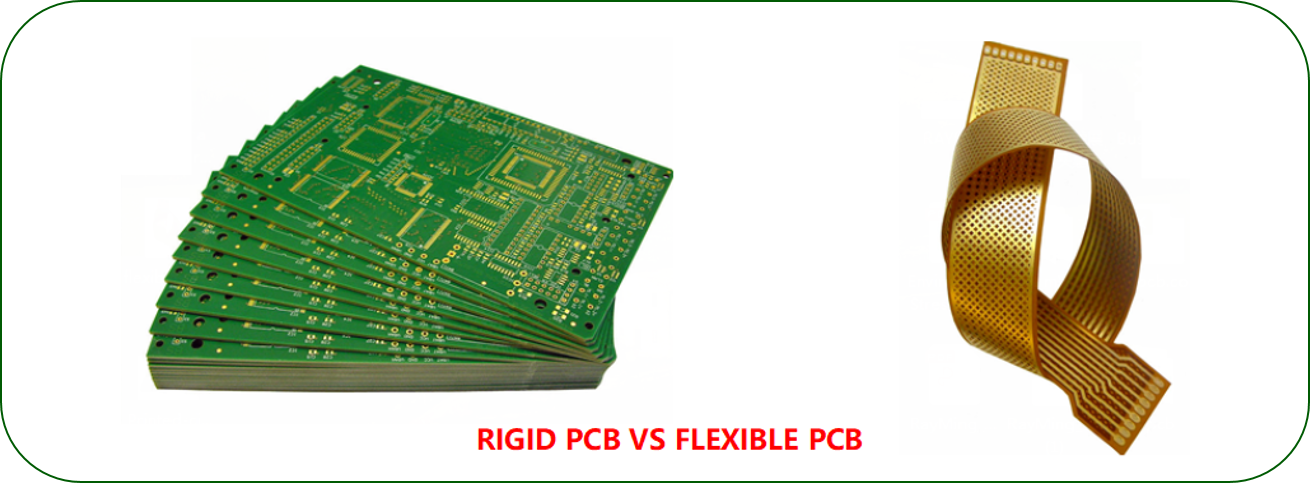
The differences between Rigid PCB And Flexible PCB
- Most of the electronics made use of traditional rigid PCB. However, technology has been evolved and many products abandoned rigid PCBs because of their inability to get folded or twisted. This has erupted the idea of flexible PCB and soon it became the prerequisite for most of the professionals in the market.
- Manufacturing process of both rigid and flexible PCBs is same with some exceptions in terms of their flexibility, softness and cost.
- Some extra measures are required for processing flex PCB when it comes to material handling. Also proper specifications are required in order to avoid any cracked solder joints when the board is bent.
- Flexible PCBs are most costly than rigid PCBs, however, we are referring here individual cost of the flexible PCB, it may happen the overall cost of the project using rigid PCB is higher than the cost of the flexible PCB, but individual cost of flexible PCB will be higher.
- Many cheap electronics make use of rigid PCBs including audio keyboards, desktop devices, solid state drives, toys and many electronic gadgets. However, flex circuits are observed in ultra high performance device because they don`t involve connectors also thinner than rigid boards and can be used in smart phones, cameras, tablets and GPS control system.
- Both rigid and flexible boards can be incorporated together to construct a unified product that comes with both strength and flexibility.
- Some flex PCBs follow the same design as rigid circuit design but they are not completely identical to the rigid circuit boards.
- Flexible PCBs provide flexible and bending solutions and they also require less space and are mostly Single-Sided PCB.
When to Use Rigid and When to Use Flexible
- Rigid PCBs typically cost less than flex circuits. I say "typically" because when considering the total cost of ownership there are some applications that, when using flexible PCBs, may be less expensive compared to using rigid PCBs. To get a true and accurate understanding of the total cost of ownership, you first need to appreciate the fact that flex circuits may eliminate the need for components such as connectors, wire harnesses, and other circuit boards. By removing these components from a design, material cost, labor and assembly cost, and scrap cost are all reduced.
- Many electronic devices (laptop and desktop computers, audio keyboards, solid-state drives (SSDs), flat-screen TVs and monitors, children`s toys, and various electronic gadgets) employ rigid PCBs instead of flexible PCBs. However, flex circuits may be found in ultra-compact and/or high-performance devices, including GPS units, tablets, smart phones, cameras, and wearables.
- Greater sophistication is not the only reason to use flex circuits; low-tech applications,such as LED lights, may utilize flex circuit technology, in some cases because it makes installation much easier.
Rigid PCB Applications
- A computer motherboard is a perfect example of rigid PCB which is a Multilayer Rigid PCB, used to distribute electricity from power supply, and creates a conducting path between CPU, GPU and RAM.
- Rigid PCBs are manufactured in volumes and once they are designed, they can not be altered or modified and remain same throughout the entire life span of the project on which they are placed.
- Some low cost products make use rigid PCBs like toys, ,electronics gadgets, desktop devices and solid state devices.
- You should also have a look at Double-Sided PCB, these are also Rigid PCBs.
Rigid Printed Circuit Board Manufacturer: Guaranteed Quick Delivery
JHYPCB is committed to providing the highest quality rigid printed circuit boards at competitive prices. As the name suggests, these PCBs use an inflexible, solid, and rigid substrate material such as fiberglass, which prohibits these boards from bending. We can provide high-quality, and performance-oriented rigid printed circuit boards in diverse specifications.
Different Types of Rigid PCB Provided by JHY PCB
- Single Sided PCB: These rigid printed circuit boards feature metal trace on single side of the dielectric. Single-sided rigid PCBs are ideal for rapid productions due to their manufacturability, as well as simple design.
- Double Sided PCB: As the name suggests, these printed circuit boards have a layer of dielectric sandwiched between two metal layers. The double-sided rigid printed circuit boards have become an industry staple. Their applications vary from low to high temperature ranges, fine line surface mounting, solder coatings, and high copper builds.
- Multilayer PCB: Multi-layer rigid PCBs feature more than two conductive metal layers, which are clearly separated by equal dielectric layers. These circuit boards allow our PCB designers to create a vast range of interconnects, as well as applications.
Learn more about JHYPCB by exploring the manufacturing capability of Rigid Printed Circuit Board below. We can do more than you can imagine.
|
Item |
Manufacturing Capability |
|
|
PCB Layers |
1-26L (TG135 TG150 TG170 TG180) |
|
|
Laminate |
FR-4, FR- 406, 370 HR ,IT180A,CEM-1, CEM-3,FR1,FR2,94HB,PTFE,etc. |
|
|
Brand of Laminate |
Kingboard,Shengyi,Nanya,Isola,Rogers,etc. |
|
|
Max Board Size |
1-2layers: 1000mm * 600mm |
|
|
Multilayer PCB: 600* 600mm |
|
|
|
Board Thickness |
0.1-4.0 mm |
|
|
Board Thickness Tolerance |
±10% |
|
|
Copper Thickness |
1-10 oz |
|
|
Min Mechanical Drilling Hole Size |
4mil(0.10mm) |
|
|
Min Laser Drilling Hole Size |
3mil(0.075mm |
|
|
Min Line Width/Line Space |
2/2mil |
|
|
Surface Finishes |
OSP, HASL, HASL Lead-Free (HASL LF), Immersion Gold(ENIG), Immersion Silver, Immersion Tin, Plated Gold, etc. |
|
|
|
||
|
Solder Mask Colors |
Green, Red, White, Black, Blue, Yellow, Orange, Purple, Gray. |
|
|
|
||
|
Silkscreen Colors |
Black, White, Yellow. |
|
|
Electrical Testing |
Fixture and Flying Probe |
|
|
Other Testing |
AOI, X-Ray(AU&NI), Two-dimension Measurement, Hole Copper Instrument, Impedance Test, Metalloscope, Peeling Strength Tester, Solderability Test, Logic Contamination Test |
|
|
Special Capabilities |
Thick Copper, Thick Gold(60μ"), Gold Finger, Blind and Buried Hole, Countersink Hole, Semi-hole, Peelable Mask, Carbon Ink, Impedance control+/- 10%, etc. |
|
Additional information
- Rigid Flex PCB Fabrication service
- Flex-Rigid PCB Technology
- Rigid Flex PCB Manufacturing Capability
- Flexible and Flex-Rigid PCB Applications
- Rigid PCB vs. Flexible PCB: How to choose?
Rigid PCB,Fr4 PCB,Rigid Circuit Board,Rigid Printed Circuit Board
JingHongYi PCB (HK) Co., Limited , https://www.pcbjhy.com