Abstract: This paper expounds the concept development of the Internet of Things and presents a universally accepted concept of the Internet of Things. It distinguishes several network concepts closely related to the Internet of Things, such as ubiquitous networks, sensor networks, and M2M. Some Internet of Things architectures compare several Internet of Things architectures and analyze the key technologies and standards of the Internet of Things.
As a new method of information dissemination, the Internet of Things has received more and more attention. People can connect as many items and networks as possible to any time and place, so as to identify, locate, track, and monitor objects, and then form intelligent solutions. This is the way of life that the Internet of Things brings to people.
1. The concept of the Internet of Things and its extension 1.1 The concept of the Internet of Things The concept of the Internet of Things was introduced in 1999 by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Auto-ID Research Center. It is the use of information sensing devices such as radio frequency identification (RFID) and other devices. The Internet is connected to enable intelligent identification and management. Constrained by the technological developments of the time, when people considered the technology of connecting objects, there was no other method besides radio frequency identification technology. At present, it is obviously unacceptable. In 2005, ITU-T released "ITU Internet Report 2005: Internet of Things", which expanded the meaning of "Internet of Things" and reported separately from the concept of the Internet of Things, related technologies, potential markets, challenges, and the world. The development opportunities and prospects for future life are elaborated on six major aspects. The report elaborates on the concept of the Internet of Things in this form: The information world and communication technology have new dimensions: anyone, any object, can be at any time. , Any place is connected in a variety of forms to create a new dynamic network - the Internet of Things.
In addition to the above two concepts of the Internet of Things, the generally accepted concept of the Internet of Things refers to the use of radio frequency identification (RFID), infrared sensing, Global Positioning System (GPS), laser scanning, and other technologies through information sensing equipment. The agreement is a network that connects any item with the Internet and carries out information exchange and communication to realize intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, monitoring and management. It is a network that extends and expands on the basis of the Internet. Perceiving, reliable transmission, and intelligent processing are the three characteristics of the Internet of Things.
1.2 Extension of the Internet of Things To understand the content of the Internet of Things, in addition to understanding the concept of the Internet of Things, it is also necessary to understand the concepts closely related to the Internet of Things, such as sensor networks, ubiquitous networks, M2M, the Internet, and mobile networks. Figure 1 shows the relationship between these concepts. The shaded part is the category of the Internet of Things.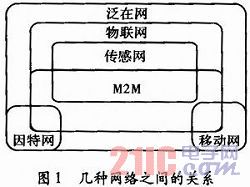
The ubiquitous network is also called the ubiquitous network and includes three levels of content: (1) The omnipresent basic network. (2) The omnipresent terminal unit. (3) omnipresent network applications. It takes 4A as the main feature, that is, it can be realized at any time (Anytime), any place (Anywhere), any person (Anyone), Anything (Anything) can easily communicate; sensor network, generally refers to the wireless sensor network WSN (Wireless Sensor Network) refers to a wireless network that is composed of randomly distributed sensor nodes, data processing units, and communication units, and is composed of self-organizing methods. The biggest difference between the sensor network and the Internet of Things is that the sensor network does not emphasize the identification of objects, but merely perceives signals, but it does not necessarily clearly identify which one of the many perceived objects; M2M refers to "machine-to-machine. "MachinetoMachine" is the most common, most common and most feasible method for implementing the Internet of Things. M2M's application covers almost all walks of life. It will be at this stage and for a long time to come. The main force of the Internet of Things research and application.
In essence, the ubiquitous network, the Internet of Things, the sensor network, and M2M actually express the same idea, that is, the expansion of information interaction from person to person to person, object, and object, thereby realizing communication. The application scope has been greatly expanded to change people’s lifestyles with “information and intelligenceâ€. The difference in concept expressions is due to the difference in the starting point of view. The ubiquitous network is mainly based on human beings. It meets people's needs through ubiquitous network composition, ubiquitous computing, and ubiquitous network applications. The sensor network focuses on the perception of information and collects, processes, and integrates data. And routing completes data support for various specific applications; M2M focuses on the communication between nodes. Through the exchange of information between nodes, machine equipment is no longer an island of information, and devices and assets are effectively monitored and managed. For the relationship between ubiquitous networks, Internet of Things, sensor networks, and M2M, the dialectical approach should be used to realize that its connotation is constantly changing.
2. The status quo of the development of the Internet of Things 2.1 The architecture of the Internet of Things The architecture of the Internet of Things has many different views in the academic community. The literature proposes that the architecture of the Internet of Things system architecture should include three levels: the perception level, the network level, and the application level. The literature proposes that the architecture of the Internet of Things architecture should include four levels: the perception layer, the transport layer, the processing layer, and the application layer. Table 1 compares the hierarchical structure of the two. The article is more in favor of the reference to the literature. It points out that the conceptual model of the Internet of Things can no longer be described using the traditional hierarchical model. The concept model of the Internet of Things is built using the three-dimensional models of items, networks, and applications, and the concept of the Internet of Things is composed of information items, autonomous networks, and intelligent applications. model. Figure 2 is a three-dimensional conceptual model of the Internet of Things. According to the literature, the layered model is used to construct the architecture and implementation model of the Internet of Things. The results obtained are relatively fragmented and need to be further classified. Theoretically, it can be shown that the Internet of Things is a complex system and cannot be constructed using a two-dimensional hierarchical model. Its logical model. Using the three-dimensional conceptual model of the Internet of Things can partly explain some of the controversies in the research and development of the Internet of Things.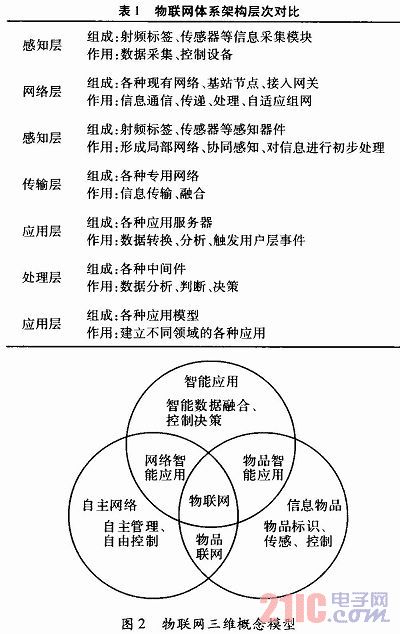
2.2 Key technologies of the Internet of Things The industrial chain of the Internet of Things can be subdivided into four areas: identification, awareness, information transmission and data processing. The core technologies include the radio frequency identification technology, sensing technology, and network and communication technologies. Data mining and fusion technologies.
(1) Radio frequency identification technology. RFID technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology that uses the radio frequency signal and its spatial coupling transmission characteristics to realize the automatic identification of static or moving objects to be identified. It is used to “standardize†the information of collection points. Since RFID technology can realize non-contact automatic identification, all-weather, strong penetrating ability, and no contact wear, it can simultaneously realize many features such as automatic identification of multiple items. This technology is applied to the field of the Internet of Things, enabling The combination of the Internet and communication technologies can enable the tracking and sharing of information across the globe, and it plays a crucial role in the "identification" of information and short-range communications. On the other hand, the product electronic code (EPC) uses RFID electronic tag technology as a carrier, which greatly promotes the development and application of the Internet of Things.
(2) Sensor technology. Information acquisition is the basis of the Internet of Things, and current information collection is mainly accomplished through sensors, sensor nodes, and electronic tags. Sensors as a detection device, as the key device for ingestion of information, because of the harsh environment in which it is located, the Internet of Things puts higher requirements on sensor technology. One is its ability to sense information, the other is the intelligence and networking of the sensor itself, and sensor technology should achieve development and breakthrough in these two aspects.
Applying the sensor to the Internet of Things can constitute a wireless autonomous network. This sensor network technology integrates sensor technology, nano-embedding technology, distributed information processing technology, and wireless communication technology, enabling various types of integrated miniaturization that can be embedded in any object. The sensors cooperate to perform real-time monitoring and collection of the measured data, and send the information to the observers in a wireless manner so as to realize “ubiquitous†sensing. In a sensor network, a sensor node has the functions of an end node and a route: First, data collection and processing are implemented, followed by data fusion and routing, and the data collected by itself and the data received by other nodes are forwarded. To other gateway nodes. The quality of the sensor node will directly affect the normal operation and function of the entire sensor network.
(3) Network and communication technologies. The realization of the Internet of Things involves short-range communication technology and long-distance transportation technology. Proximity communication technology involves RFID, Bluetooth, etc. Remote transport technology involves the Internet's networking, gateways and other technologies.
As the basic channel for providing information transmission and service support for the Internet of Things, by enhancing the professional and interconnected functions of existing network communication technologies to meet the business needs of the Internet of Things with low mobility and low data rate, the information can be transmitted safely and reliably. , is a focus of the current research on the Internet of Things. Sensor network communication technologies mainly include wide-area network communication and near-field communication. Wide-area areas mainly include IP Internet, 2G/3G mobile communication, and satellite communication technologies. The development of new networking with iPv6 as the core is even more important. The Internet of Things (IoT) provides efficient delivery channels. In terms of close distance, the current mainstream is the short-range communication technology represented by IEEE 802.15.4.
M2M technology is also the key to the realization of the Internet of Things. The long-distance connection technologies that can be combined with M2M technologies include GSM, GPRS, and UMTS. The close-range connection technologies such as WIFI, Bluetooth, ZigBee, RFID, and UWB can also be combined with XML, Corba, and GPS. , wireless terminal and network location service technology. M2M can be used in security monitoring, vending machines, cargo tracking, and is widely used.
(4) Data mining and integration. From the perception layer to the application layer of the Internet of Things, the variety and quantity of various information are exponentially increased. The amount of data that needs to be analyzed also increases in number of stages. It also involves data from various heterogeneous networks or between multiple systems. Fusion issues, how to timely find out hidden information and effective data from massive data, brought huge challenges to data processing. Therefore, how to reasonably and effectively integrate, mine, and intelligently process massive amounts of data is a problem for the Internet of Things. . Combining distributed computing technologies such as P2P and cloud computing has become a way to solve the above problems. Cloud computing provides a new, highly efficient computing model for the Internet of Things. It can provide on-demand, scalable, and inexpensive computing over the Internet. It has a relatively reliable and secure data center. It also has the convenience, cheapness, and mainframe of Internet services. The ability to easily share data and applications between different devices, users do not need to worry about information disclosure, hacking and other thorny issues. Cloud computing is a milestone in the development of informatization. It emphasizes the aggregation, optimization, and dynamic allocation of information resources, saves informationization costs, and greatly increases the efficiency of data centers.
2.3 Status Quo of IoT Standards Due to the wide range of content and technologies involved in the Internet of Things, there are many international organizations that participate in IoT standards development. No one organization has yet developed a complete IoT standard system. Table 2 lists the major international standards development organizations and their research directions.
The standard organizations for studying the Internet of Things in China mainly include the Sensor Network Standards Working Group (WGSN) and the China Communications Standards Association (CCSA). WGSN is a national technical organization that has been approved by the National Standardization Management Committee for the preparation and establishment of the National Standardization Technical Committee for Information Technology, and has been established and led by the National Information Technology Standardization Technical Committee. At present, WGSN has established a number of standards development project groups. Among them, collaborative information processing support services and interfaces have promoted a new work project in the International Organization for Standardization. In March 2010, this standard has passed new work projects. Voting will start the formulation of international standardization. In 2010, CCSA established the ubiquitous network technology working committee (TC10), which specializes in research related to the Internet of Things. It has launched the “Ubiquitous Wireless Network Architecture†and “Gateway Device Technology Combining Wireless Sensor Networks and Telecom Networksâ€. "Requirements" and other standards for research and development, but no standard manuscript has yet been published.
3. Concluding remarks With the continuous maturation and improvement of technology, standards and systems, the Internet of Things will bring convenience to people's lifestyle. However, the development of the Internet of Things is still in its infancy. There are still certain problems in the implementation process, such as security, standards, business models, etc. It is necessary to work hard to overcome the core technologies and to establish the Internet of Things international standard and a series of corresponding supporting legal norms as soon as possible. It will be perfected.
As a new method of information dissemination, the Internet of Things has received more and more attention. People can connect as many items and networks as possible to any time and place, so as to identify, locate, track, and monitor objects, and then form intelligent solutions. This is the way of life that the Internet of Things brings to people.
1. The concept of the Internet of Things and its extension 1.1 The concept of the Internet of Things The concept of the Internet of Things was introduced in 1999 by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Auto-ID Research Center. It is the use of information sensing devices such as radio frequency identification (RFID) and other devices. The Internet is connected to enable intelligent identification and management. Constrained by the technological developments of the time, when people considered the technology of connecting objects, there was no other method besides radio frequency identification technology. At present, it is obviously unacceptable. In 2005, ITU-T released "ITU Internet Report 2005: Internet of Things", which expanded the meaning of "Internet of Things" and reported separately from the concept of the Internet of Things, related technologies, potential markets, challenges, and the world. The development opportunities and prospects for future life are elaborated on six major aspects. The report elaborates on the concept of the Internet of Things in this form: The information world and communication technology have new dimensions: anyone, any object, can be at any time. , Any place is connected in a variety of forms to create a new dynamic network - the Internet of Things.
In addition to the above two concepts of the Internet of Things, the generally accepted concept of the Internet of Things refers to the use of radio frequency identification (RFID), infrared sensing, Global Positioning System (GPS), laser scanning, and other technologies through information sensing equipment. The agreement is a network that connects any item with the Internet and carries out information exchange and communication to realize intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, monitoring and management. It is a network that extends and expands on the basis of the Internet. Perceiving, reliable transmission, and intelligent processing are the three characteristics of the Internet of Things.
1.2 Extension of the Internet of Things To understand the content of the Internet of Things, in addition to understanding the concept of the Internet of Things, it is also necessary to understand the concepts closely related to the Internet of Things, such as sensor networks, ubiquitous networks, M2M, the Internet, and mobile networks. Figure 1 shows the relationship between these concepts. The shaded part is the category of the Internet of Things.

The ubiquitous network is also called the ubiquitous network and includes three levels of content: (1) The omnipresent basic network. (2) The omnipresent terminal unit. (3) omnipresent network applications. It takes 4A as the main feature, that is, it can be realized at any time (Anytime), any place (Anywhere), any person (Anyone), Anything (Anything) can easily communicate; sensor network, generally refers to the wireless sensor network WSN (Wireless Sensor Network) refers to a wireless network that is composed of randomly distributed sensor nodes, data processing units, and communication units, and is composed of self-organizing methods. The biggest difference between the sensor network and the Internet of Things is that the sensor network does not emphasize the identification of objects, but merely perceives signals, but it does not necessarily clearly identify which one of the many perceived objects; M2M refers to "machine-to-machine. "MachinetoMachine" is the most common, most common and most feasible method for implementing the Internet of Things. M2M's application covers almost all walks of life. It will be at this stage and for a long time to come. The main force of the Internet of Things research and application.
In essence, the ubiquitous network, the Internet of Things, the sensor network, and M2M actually express the same idea, that is, the expansion of information interaction from person to person to person, object, and object, thereby realizing communication. The application scope has been greatly expanded to change people’s lifestyles with “information and intelligenceâ€. The difference in concept expressions is due to the difference in the starting point of view. The ubiquitous network is mainly based on human beings. It meets people's needs through ubiquitous network composition, ubiquitous computing, and ubiquitous network applications. The sensor network focuses on the perception of information and collects, processes, and integrates data. And routing completes data support for various specific applications; M2M focuses on the communication between nodes. Through the exchange of information between nodes, machine equipment is no longer an island of information, and devices and assets are effectively monitored and managed. For the relationship between ubiquitous networks, Internet of Things, sensor networks, and M2M, the dialectical approach should be used to realize that its connotation is constantly changing.
2. The status quo of the development of the Internet of Things 2.1 The architecture of the Internet of Things The architecture of the Internet of Things has many different views in the academic community. The literature proposes that the architecture of the Internet of Things system architecture should include three levels: the perception level, the network level, and the application level. The literature proposes that the architecture of the Internet of Things architecture should include four levels: the perception layer, the transport layer, the processing layer, and the application layer. Table 1 compares the hierarchical structure of the two. The article is more in favor of the reference to the literature. It points out that the conceptual model of the Internet of Things can no longer be described using the traditional hierarchical model. The concept model of the Internet of Things is built using the three-dimensional models of items, networks, and applications, and the concept of the Internet of Things is composed of information items, autonomous networks, and intelligent applications. model. Figure 2 is a three-dimensional conceptual model of the Internet of Things. According to the literature, the layered model is used to construct the architecture and implementation model of the Internet of Things. The results obtained are relatively fragmented and need to be further classified. Theoretically, it can be shown that the Internet of Things is a complex system and cannot be constructed using a two-dimensional hierarchical model. Its logical model. Using the three-dimensional conceptual model of the Internet of Things can partly explain some of the controversies in the research and development of the Internet of Things.

2.2 Key technologies of the Internet of Things The industrial chain of the Internet of Things can be subdivided into four areas: identification, awareness, information transmission and data processing. The core technologies include the radio frequency identification technology, sensing technology, and network and communication technologies. Data mining and fusion technologies.
(1) Radio frequency identification technology. RFID technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology that uses the radio frequency signal and its spatial coupling transmission characteristics to realize the automatic identification of static or moving objects to be identified. It is used to “standardize†the information of collection points. Since RFID technology can realize non-contact automatic identification, all-weather, strong penetrating ability, and no contact wear, it can simultaneously realize many features such as automatic identification of multiple items. This technology is applied to the field of the Internet of Things, enabling The combination of the Internet and communication technologies can enable the tracking and sharing of information across the globe, and it plays a crucial role in the "identification" of information and short-range communications. On the other hand, the product electronic code (EPC) uses RFID electronic tag technology as a carrier, which greatly promotes the development and application of the Internet of Things.
(2) Sensor technology. Information acquisition is the basis of the Internet of Things, and current information collection is mainly accomplished through sensors, sensor nodes, and electronic tags. Sensors as a detection device, as the key device for ingestion of information, because of the harsh environment in which it is located, the Internet of Things puts higher requirements on sensor technology. One is its ability to sense information, the other is the intelligence and networking of the sensor itself, and sensor technology should achieve development and breakthrough in these two aspects.
Applying the sensor to the Internet of Things can constitute a wireless autonomous network. This sensor network technology integrates sensor technology, nano-embedding technology, distributed information processing technology, and wireless communication technology, enabling various types of integrated miniaturization that can be embedded in any object. The sensors cooperate to perform real-time monitoring and collection of the measured data, and send the information to the observers in a wireless manner so as to realize “ubiquitous†sensing. In a sensor network, a sensor node has the functions of an end node and a route: First, data collection and processing are implemented, followed by data fusion and routing, and the data collected by itself and the data received by other nodes are forwarded. To other gateway nodes. The quality of the sensor node will directly affect the normal operation and function of the entire sensor network.
(3) Network and communication technologies. The realization of the Internet of Things involves short-range communication technology and long-distance transportation technology. Proximity communication technology involves RFID, Bluetooth, etc. Remote transport technology involves the Internet's networking, gateways and other technologies.
As the basic channel for providing information transmission and service support for the Internet of Things, by enhancing the professional and interconnected functions of existing network communication technologies to meet the business needs of the Internet of Things with low mobility and low data rate, the information can be transmitted safely and reliably. , is a focus of the current research on the Internet of Things. Sensor network communication technologies mainly include wide-area network communication and near-field communication. Wide-area areas mainly include IP Internet, 2G/3G mobile communication, and satellite communication technologies. The development of new networking with iPv6 as the core is even more important. The Internet of Things (IoT) provides efficient delivery channels. In terms of close distance, the current mainstream is the short-range communication technology represented by IEEE 802.15.4.
M2M technology is also the key to the realization of the Internet of Things. The long-distance connection technologies that can be combined with M2M technologies include GSM, GPRS, and UMTS. The close-range connection technologies such as WIFI, Bluetooth, ZigBee, RFID, and UWB can also be combined with XML, Corba, and GPS. , wireless terminal and network location service technology. M2M can be used in security monitoring, vending machines, cargo tracking, and is widely used.
(4) Data mining and integration. From the perception layer to the application layer of the Internet of Things, the variety and quantity of various information are exponentially increased. The amount of data that needs to be analyzed also increases in number of stages. It also involves data from various heterogeneous networks or between multiple systems. Fusion issues, how to timely find out hidden information and effective data from massive data, brought huge challenges to data processing. Therefore, how to reasonably and effectively integrate, mine, and intelligently process massive amounts of data is a problem for the Internet of Things. . Combining distributed computing technologies such as P2P and cloud computing has become a way to solve the above problems. Cloud computing provides a new, highly efficient computing model for the Internet of Things. It can provide on-demand, scalable, and inexpensive computing over the Internet. It has a relatively reliable and secure data center. It also has the convenience, cheapness, and mainframe of Internet services. The ability to easily share data and applications between different devices, users do not need to worry about information disclosure, hacking and other thorny issues. Cloud computing is a milestone in the development of informatization. It emphasizes the aggregation, optimization, and dynamic allocation of information resources, saves informationization costs, and greatly increases the efficiency of data centers.
2.3 Status Quo of IoT Standards Due to the wide range of content and technologies involved in the Internet of Things, there are many international organizations that participate in IoT standards development. No one organization has yet developed a complete IoT standard system. Table 2 lists the major international standards development organizations and their research directions.

The standard organizations for studying the Internet of Things in China mainly include the Sensor Network Standards Working Group (WGSN) and the China Communications Standards Association (CCSA). WGSN is a national technical organization that has been approved by the National Standardization Management Committee for the preparation and establishment of the National Standardization Technical Committee for Information Technology, and has been established and led by the National Information Technology Standardization Technical Committee. At present, WGSN has established a number of standards development project groups. Among them, collaborative information processing support services and interfaces have promoted a new work project in the International Organization for Standardization. In March 2010, this standard has passed new work projects. Voting will start the formulation of international standardization. In 2010, CCSA established the ubiquitous network technology working committee (TC10), which specializes in research related to the Internet of Things. It has launched the “Ubiquitous Wireless Network Architecture†and “Gateway Device Technology Combining Wireless Sensor Networks and Telecom Networksâ€. "Requirements" and other standards for research and development, but no standard manuscript has yet been published.
3. Concluding remarks With the continuous maturation and improvement of technology, standards and systems, the Internet of Things will bring convenience to people's lifestyle. However, the development of the Internet of Things is still in its infancy. There are still certain problems in the implementation process, such as security, standards, business models, etc. It is necessary to work hard to overcome the core technologies and to establish the Internet of Things international standard and a series of corresponding supporting legal norms as soon as possible. It will be perfected.
Uni Flange,Forging High Neck Flange,Flanged Joint,Stainless Steel Flange
Zhangqiu Xinhao Machinery Parts Factory , https://www.xhflange.com