
904L is an austenitic stainless steel known for its excellent corrosion resistance across a wide range of environments. This alloy is specifically designed to withstand harsh conditions, thanks to its unique composition. Its austenitic structure ensures high toughness and strength even at sub-zero temperatures, making it ideal for challenging applications.
Table of contents
- Stainless Steel 904L Chemical Composition
- SS 904L Mechanical Properties
- Physical properties of INOX AISI 904L
- AISI 904L Welding Process
- SUS 904L Mean Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
- Corrosion Resistance of Alloy 904l
- Corrosion Rates of 904L Material
- Chemical Compatibility of Stainless Steel Alloy 904L
- UNS N08904 Material Temperature Range
- Type 904L Stainless Steel Thermal Properties
- AISI 904L Equivalent grades
- Specifications of SUS 904l Material
- SAE 904l Electrical Properties
- Din 1.4539 Applications
- Advantages & Disavntages of SS 904l Material
- Hot Forming of SUS 904l
- Cold Forming of SS 904L
- Machining of Stainless Steel Alloy 904L

Stainless Steel 904L Chemical Composition
SS 904L Mechanical Properties
| Grade | Yield Strength 0.2% Proof (MPa) min | Tensile Strength (MPa) min | Elongation (% in 50mm) min | Hardness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brinell (HB) | Rockwell B (HR B) | ||||
| 904L | 220 | 490 | 36 | 150 | 70-90 typical |
Physical properties of INOX AISI 904L
| Density | kg/dm³ | 8 |
|---|---|---|
| Modulus of elasticity | GPa | 195 |
| Thermal Capacity | J/kg°C | 450 |
| Electrical resistivity | µΩm | 1 |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m°C | 15.8 |
Alloy 904l Offers Excellent Formability and Weldability
Being non-magnetic, 904L offers exceptional formability and weldability, making it easy to shape and join into various configurations without compromising its integrity. This property allows the material to be used in a wide range of industrial applications where precise shaping and strong joints are required.
AISI 904L Welding Process
- TIG
- MIG
- SMAW
- PAW
- SAW

SUS 904L Mean Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
| Yield Strength 0.2% Offset psi (MPa) | Ultimate Tensile Strength psi (MPa) | Hardness | Elongation in 2 in. % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31,000 | 220 | 71,000 | 490 | 70 – 90 Rockwell B | 36 |
1.4539 Material is Known for Its Corrosion Properties
As a low-carbon, high-alloy austenitic stainless steel, 904L is widely used for its superior corrosion resistance. The presence of copper enhances its performance in acidic environments such as sulfuric, phosphoric, and acetic acid. It also shows high resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride solutions and is less prone to stress corrosion cracking.
Corrosion Resistance of Alloy 904l
- Good Resistance to Uniform Corrosion
- Temperatures up to 95°F (35°C)
- Concentration Range of 0 to 100%.
- A Nickel content of 25%, 904L is a good Alternative
- Susceptible to Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking
- 904L Have Good Resistance to SCC
Minimum Stress For Failure % of Rp0.2 at 200°C
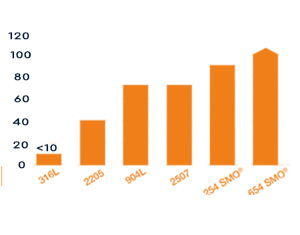
Typical threshold stresses determined using the drop evaporation test.
Temperature, °C
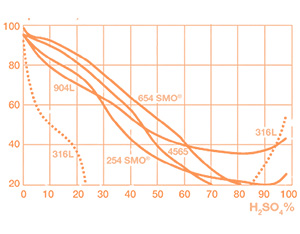
Isocorrosion curves 0.1 mm/year, in pure sulphuric acid.
Corrosion Rates of 904L Material
| Uniform corrosion | Corrosion, (mm/year) |
|---|---|
| pickling acid at 25°C | 0.47 |
| wet process Phosphoric acid at 60°C | 1.2 |
| Distillation of Tall oil at 253°C | 0.06 |
SUS 904l Has High Concentrations of Chromium, Nickel and Molybdenum
Its high alloyed chemical composition ensures excellent corrosion resistance, with nickel and molybdenum offering good resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking, pitting, and general corrosion. This makes it suitable for use in aggressive environments where other materials may fail.
Chemical Compatibility of Stainless Steel Alloy 904L
| Chemical | Compatibility |
|---|---|
| Sulfuric Acid (Hâ‚‚SOâ‚„) | Good resistance ; avoid concentrated acid. |
| Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) | Better resistance compared to many other stainless steels, especially at lower temperatures. |
| Nitric Acid (HNO₃) | Good resistance, particularly up to 65% concentration at room temperature. |
| Phosphoric Acid (H₃PO₄) | Good performance in moderate concentrations and temperatures. |
| Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) | Resistant, especially in lower concentrations |
| Sodium Chloride (NaCl) | Resistant but prone to stress corrosion cracking in high chloride environments. |
| Acetone | Generally compatible. |
| Ethanol | Generally compatible. |
| Formic Acid | Shows good resistance. |
| Oxidizing Agents | Resistant to many oxidizing agents. |
| Hydrogen Sulfide (Hâ‚‚S) | Susceptible to stress corrosion cracking, especially under high temperature. |
SS 904l is Heat Resistant Alloy Designed for High Temperature Structural Applications
This material is ideal for use in high-temperature environments due to its remarkable heat and corrosion resistance. It can maintain its structural integrity in harsh conditions, making it suitable for industries like chemical and petrochemical, where both high temperatures and corrosive substances are common.
UNS N08904 Material Temperature Range
| Temperature Range | Performance |
|---|---|
| Cryogenic Temperatures (< -200°C / -328°F) | Generally suitable |
| Ambient to Moderate Temperatures (up to ~400°C / 750°F) | Excellent performance |
| High Temperatures (~400°C to 800°C / 750°F to 1470°F) | Capable of withstanding moderate temperatures |
| Exceeding 800°C / 1470°F | The material is generally not recommended for such high temperatures. |
Type 904L Stainless Steel Thermal Properties
| Thermal Properties | Metric | English |
|---|---|---|
| CTE, linear | 15.3 µm/m-°C Temperature 20.0 – 100 °C |
8.50 µin/in-°F Temperature 68.0 – 212 °F |
| 16.5 µm/m-°C Temperature 20.0 – 400 °C |
9.17 µin/in-°F Temperature 68.0 – 752 °F |
|
| 18.2 µm/m-°C Temperature 20.0 – 800 °C |
10.1 µin/in-°F Temperature 68.0 – 1470 °F |
|
| Specific Heat Capacity | 0.460 J/g-°C | 0.110 BTU/lb-°F |
| Thermal Conductivity | 11.5 W/m-K Temperature 20.0 °C |
79.8 BTU-in/hr-ft²-°F Temperature 68.0 °F |
| 12.9 W/m-K Temperature 100 °C |
89.5 BTU-in/hr-ft²-°F Temperature 212 °F |
Refer 904l Material Equivalent, Composition and Specification
The equivalent grade of 904L helps users identify the same material across different standards and regions, facilitating international trade and ensuring consistency in application. Understanding the composition is essential for determining the material's mechanical and corrosion-resistant properties, which directly impact its suitability for specific uses.
Specifications provide standardized data on the material’s characteristics, helping engineers and designers select the right grade for their projects. This information ensures that the material meets the necessary requirements for performance and reliability in its intended application.
AISI 904L Equivalent grades
| Grade | UNS No | Old British | Swedish SS | Euronorm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| En | BS | No | Name | |||
| 904L | N08904 | – | 904S13 | 2562 | 1.4539 | X1NiCrMoCuN25-20-5 |
Specifications of SUS 904l Material
- Trade Names :SS 904L, AISI 904L, INOX 904L, SUS 904L, Stainless Steel 904L, 904L Steel, ASTM 904L
- Benefits :Non-magnetic, Excellent corrosion properties, Good resistance to sulphuric, Excellent formability and weldability
- Tempraturer Range :850 °C – 1150 °C
- Features :Lower carbon content leads to resistance to sensitization when welded, Increased resistance to chemical attack from acids
SAE 904l Electrical Properties
| Electrical Properties | Metric | English |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.0000952 ohm-cm | 0.0000952 ohm-cm |
| Magnetic Permeability | <= 1.02 | <= 1.02 |
Din 1.4539 Applications
- Organic Acid Treatment System
- Sea Water Heat Exchanger
- Paper Industry Equipment
- Heat Exchangers
- Condenser Tubes
- Gas Scrubbing Plants
- Pulp and Paper Processing Industries
Advantages & Disavntages of SS 904l Material
Advantages
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance
- Good Strength and Toughness
- Good Formability & Durability
- It is Non-magnetic in the Annealed Condition
Disadvantages
- Expensive Material
- Not Ideal for Very High Temperatures
- Extremely High-temperature Applications
- Potential for Work Hardening
Hot Forming of SUS 904l
- Working temperatures:1562 – 2102°F (850 –1150°C)
- Forming Techniques:Forging, rolling, or extrusion
- Solution Annealed:1940 – 2084°F (1060 –1140°C).
- Partial Heating or Cooling :below 2012°F (1100°C)
Cold Forming of SS 904L
- Work Hardening: work-hardens significantly, cold working might require intermediate annealing.
- Nitrogen Implies more powerful processing equipment
- Ductile and Forms Easily
Machining of Stainless Steel Alloy 904L
- Makes it less Machinable
- More Challenging due to work hardening
- Using proper tooling and cutting fluids.
It can also carry out bulldozing, lifting and loading and unloading of other materials such as wood by changing different auxiliary working devices.In the construction of roads, especially high-grade highways, wheel loaders are used for filling and excavation of roadbed engineering, asphalt mixture and aggregate and loading of cement concrete yards.Still can undertake pushing ground of carry soil, strickle and drawing in addition the exercise such as other machine.Because wheel loader has operating speed fast, efficiency tall, maneuverability good, operation is light wait for an advantage, the main machine that accordingly it makes construction of the cubic metro of earth and stone in project is planted one of.
The tire loading machine is composed of power unit, frame, running gear, transmission system, steering system, braking system, hydraulic system and working device.The tire loader adopts a diesel engine as the power device, a hydraulic mechanical transmission system composed of a hydraulic torque converter, a power shift gearbox, and a double-axle drive (some small tire loaders use hydraulic transmission or mechanical transmission), hydraulic Steering, articulated frame steering, working device for reverse rod mechanism.
Wheel Loader,Compact Wheel Loader,loader for sale,Mini Wheel Loader
Shandong Vio Machinery co.,ltd. , https://www.shantui-xcmgparts.com